A Brief History of the Stock Market – 1792
🕰️ Quick Summary
- 📈 The stock market has evolved over 400+ years from a merchant-driven exchange to a global economic engine.
- 💡 Key milestones include the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, the Buttonwood Agreement, and the rise of electronic trading.
- 📚 Case studies and expert commentary provide practical insights for today’s investors.
📌 Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Amsterdam Exchange: Birthplace of the Market
- The Rise of the London Stock Exchange
- Wall Street and the Buttonwood Agreement
- The Digital Era of Trading
- Case Studies & Real-Life Examples
- Key Takeaways
- FAQ
- Further Reading
📖 Introduction
The stock market is more than just a place to trade shares—it is the heartbeat of modern capitalism. From its humble beginnings in 17th-century Europe to today’s high-frequency algorithms, the evolution of stock trading reflects humanity’s progress, innovation, and greed alike.
Quote of the Day: “The four most dangerous words in investing are: ‘This time it’s different.’” – Sir John Templeton
If you’ve ever wondered how we went from trading tulip bulbs to crypto futures and AI-led strategies:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}, this guide is for you.
🏛️ The Amsterdam Exchange: Birthplace of the Market
Most historians agree that the world’s first official stock market was established in Amsterdam in 1602, when the Dutch East India Company (VOC) began issuing shares to the public. This was revolutionary—it allowed regular citizens to invest in long sea voyages and exotic trade routes.
Investopedia refers to it as the first modern stock exchange—a centralized venue where buyers and sellers could meet.
Traders would gather in coffee houses and at the town square to negotiate, setting the groundwork for modern exchanges. Many of these lessons carry over to today’s methods, including strategies we discuss in this post on stock ownership:contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}.
🇬🇧 The Rise of the London Stock Exchange
In the 1690s, stock trading migrated to London’s Exchange Alley. Similar to Amsterdam, brokers met in coffeehouses like Jonathan’s to conduct trades. By 1801, the London Stock Exchange (LSE) had become a formalized institution and rivaled Amsterdam in sophistication.
What’s interesting is how scandals shaped regulation. The infamous South Sea Bubble of 1720, where stock manipulation caused widespread financial ruin, led to early financial oversight—something echoed in modern policies around speculative trading like volume-based strategies:contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2}.
“History doesn’t repeat itself, but it often rhymes.” – Mark Twain (as quoted in Financial Times)

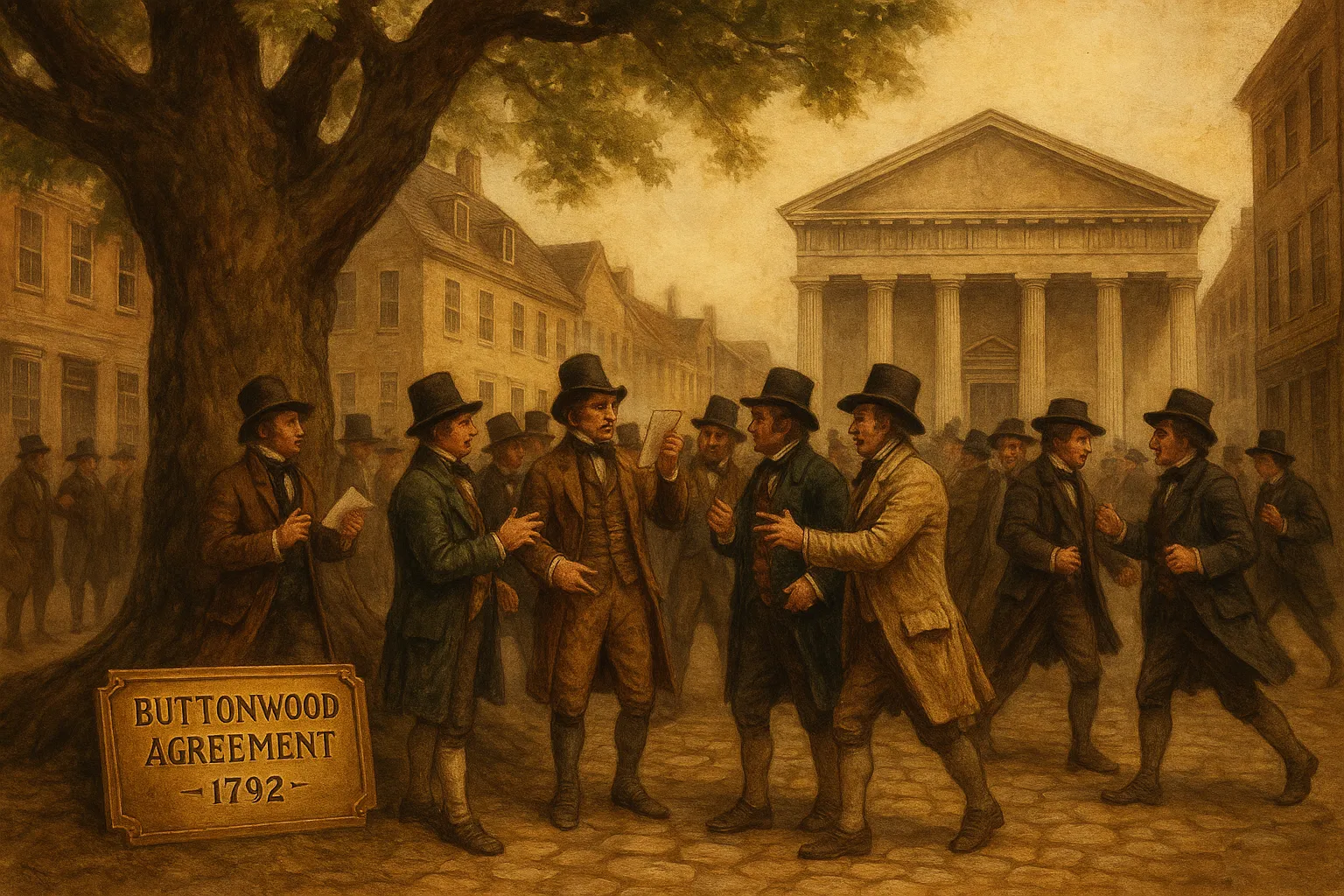
📉 Wall Street and the Buttonwood Agreement
Modern U.S. trading began in 1792 when 24 stockbrokers signed the Buttonwood Agreement under a tree on Wall Street. This pact eventually gave birth to the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
Originally focused on government bonds and a few bank stocks, the NYSE grew rapidly after the Industrial Revolution. By the early 1900s, major corporations like Ford, Standard Oil, and General Electric were listed, fueling public interest in investing.
As investor interest surged, so did market volatility. The 1929 crash was a defining moment, prompting the U.S. government to create the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and tighter regulations—many of which continue to influence how platforms like Swing Trade Bot operate today:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}.
“The NYSE wasn’t born from algorithms—it was born under a tree.” — Michael Selden, Financial Historian
💻 The Digital Era of Trading
In the 1970s and 1980s, technology revolutionized the markets. NASDAQ launched in 1971 as the world’s first electronic stock exchange. Electronic trading removed physical barriers, allowing traders worldwide to participate with speed and precision.
Fast forward to the 2000s, and algorithmic trading, robo-advisors, and mobile apps reshaped how we interact with the market. Today’s traders rely on platforms, AI, and community resources such as Swing Trading Chat Rooms for rapid decision-making:contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}.
As CNBC reports, algorithms now make up over 70% of trading volume in U.S. equities.

✅ Pros and ❌ Cons of Stock Market Evolution
| ✔️ Democratized access to investing | ❌ Subject to speculation and bubbles |
| ✔️ Transparent pricing and liquidity | ❌ High-frequency trading can distort markets |
| ✔️ Long-term wealth generation | ❌ Emotional investing still drives poor decisions |
Dr. Sarah Ng, Economist at MarketWatch: “Understanding the stock market’s history allows you to better anticipate its future patterns—and avoid its most common traps.”
This insight aligns closely with our article on how to identify bad stock news:contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2}—a skill more important than ever in today’s algorithm-fueled markets.
📊 Case Studies & Real-Life Examples
Case Study: The Dot-Com Bubble (1995–2001)
In the late 1990s, investors poured money into internet companies, driving valuations sky-high without profits. When reality set in, the market crashed. Lessons learned: Always analyze fundamentals—just as discussed in how to tell what stock is suitable for you:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}.
Case Study: The GameStop Short Squeeze (2021)
In early 2021, Reddit traders initiated a short squeeze on GameStop, forcing hedge funds to cover losses. This event highlighted the power of retail traders and community coordination—topics we explore further in our penny stock alerts guide:contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}.
🧠 Key Takeaways
- 📌 The stock market evolved from physical exchanges to lightning-fast digital platforms.
- 📌 History shows that speculative manias often precede reform.
- 📌 Understanding the market’s past can help investors make smarter, more disciplined decisions today.
- 📌 Tools like strategy PDFs:contentReference[oaicite:2]{index=2} and community tools enhance modern investing.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Q: When did stock markets first begin?
A: In 1602 with the Dutch East India Company issuing shares on the Amsterdam Exchange.
Q: What caused the biggest crashes?
A: Over-leverage, speculative manias, and investor psychology—highlighted in events like 1929 and 2008.
Q: Has technology helped or hurt trading?
A: Both. It increased access and speed but introduced volatility and automation risks.
📚 Further Reading
- How to Invest Smartly for Long-Term Growth:contentReference[oaicite:3]{index=3}
- Stock Market Courses for Beginners:contentReference[oaicite:4]{index=4}
- SEC Investor Education Resources
- NYSE Official Site
- NASDAQ History and About Page

🔍 Expert Resources to Deepen Your Knowledge
We’ve curated a set of authoritative, high-trust resources to help you further explore the history and function of the stock market. These external links complement everything you’ve read so far—bringing in diverse perspectives from academics, regulators, and finance professionals.
📘 Investopedia – Stock Market History
One of the most comprehensive guides on how the stock market began and evolved globally.
Read More →📈 NYSE – Our History
Learn about the origins of the New York Stock Exchange straight from the source.
Visit NYSE →📊 Nasdaq – Market Evolution
Explore how Nasdaq shaped modern electronic trading systems across global markets.
Explore Nasdaq →🧠 Financial Times – Market History Deep Dive
Understand how the market has adapted across centuries—from bubbles to breakthroughs.
Read FT Market Coverage →🔒 SEC – U.S. Securities Regulation
For a government-backed perspective on market structure, rules, and investor protections.
Visit SEC.gov →🔗 Bookmark & Share This Resource
If this guide helped you understand the evolution of the stock market, consider sharing it with your audience or bookmarking it for future reference. Knowledge compounds—just like your investments.
🔧 Bonus FAQs
- Q: Where was the world’s first stock market founded?
- A: In Amsterdam, Netherlands, in 1602, when the Dutch East India Company issued public shares.
- Q: When did the U.S. stock market officially begin?
- A: In 1792 with the Buttonwood Agreement, which formed the basis of the New York Stock Exchange.
- Q: What’s the difference between NYSE and Nasdaq?
- A: NYSE is an auction-based exchange, while Nasdaq is an electronic quote-driven system.