
What Determines the Value of Options? 7 Powerful Factors
What Determines the Value of Options? 7 Powerful Factors
The value of options is one of the most debated topics in trading. Every investor—from Wall Street veterans to retail traders—faces the same challenge: understanding why an option is priced the way it is. Without this knowledge, traders risk overpaying for contracts, mismanaging risk, and missing profitable opportunities.
At its core, an option’s value is shaped by both intrinsic factors (like the relationship between stock price and strike price) and extrinsic factors (such as time decay and volatility). To succeed, you must master both sides of this equation.
“In investing, what is comfortable is rarely profitable.”— Robert Arnott
💡 Why Options Value Matters
Unlike stocks, which represent direct ownership of a company, options are derivatives—their worth depends entirely on something else. That means a trader’s edge comes from identifying how the underlying market forces determine pricing.
According to Investopedia’s Options Guide , understanding these forces is crucial for both hedging and speculation. A well-priced option can protect your portfolio during downturns, while a poorly priced one can magnify losses.
📊 A Quick Case Study
In 2020, during the pandemic-driven market crash, many traders who didn’t understand the mechanics of time value and volatility ended up buying calls at inflated prices. As volatility fell in the following weeks, these options collapsed in value—even when the stock recovered. This real-world scenario shows how failing to grasp the value of options can turn what looks like a winning trade into a losing one.
🔗 Related Reading
If you’re just starting out, you may want to first review the fundamentals of stock market investing before diving deeper into options pricing. This foundation will make the advanced concepts in this guide much easier to understand.
In the following sections, we’ll break down the 7 powerful factors that determine the value of options. From time decay to market psychology, these are the forces that every trader must understand to thrive in options trading.
Factor 1: Intrinsic Value & Stock Price Movement
The most fundamental driver of the value of options is intrinsic value. In simple terms, intrinsic value reflects how much profit an option would generate if exercised immediately. Everything else—volatility, time, sentiment—layers on top of this foundation.
📌 Understanding Intrinsic Value
– A call option has intrinsic value when the stock price is above the strike price. – A put option has intrinsic value when the stock price is below the strike price. – If the option would result in no profit if exercised today, it is considered out-of-the-money (OTM) and has zero intrinsic value.
📊 Real-World Example
Imagine Apple (AAPL) is trading at $200. – A $190 call option has $10 of intrinsic value because the right to buy at $190 is already $10 cheaper than the market. – A $210 call option has zero intrinsic value because the stock is still below the strike. This simple relationship is why stock movement is the core engine of options pricing.
“Price is what you pay. Value is what you get.”— Warren Buffett
🔗 Related Resources
A deeper understanding of company value can also help in options trading. See our guide on understanding the real value of a stock for context on how stock prices are assessed fundamentally. For a more technical breakdown of strike vs market prices, the CME Group’s options education provides clear examples from the futures and options markets.
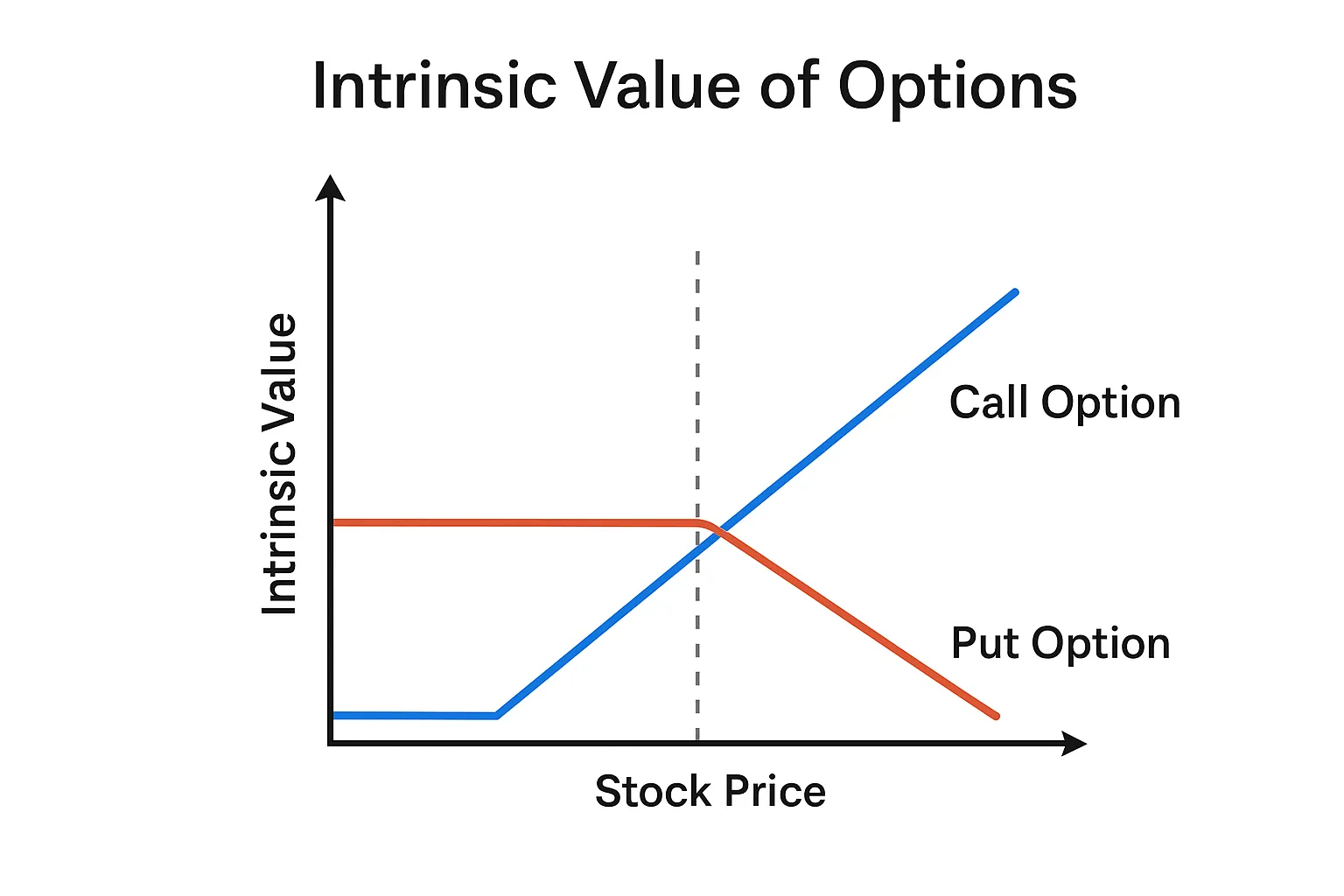
Description: A chart showing intrinsic value curves for call and put options, illustrating how value rises once the strike is surpassed.
⚖️ Why It Matters
Many new traders focus only on volatility or time decay, but without stock movement in their favor, an option can never become profitable. Intrinsic value is what separates winning trades from wasted premiums.
Factor 2: Time Value & The Impact of Decay
If intrinsic value is the skeleton of an option, time value is the living tissue around it. Time value—also called extrinsic value—represents the added premium investors pay for the possibility that an option becomes profitable before expiration.
⏳ What Is Time Value?
The more time an option has until expiration, the greater the chance the underlying stock might move in the trader’s favor. This is why a three-month call option on Tesla costs more than a one-week call with the same strike price. Extra time = extra opportunity.
⚡ The Decay Effect (Theta)
Time value doesn’t last forever. It gradually erodes due to a process traders call Theta decay. As expiration approaches, time value decays at an accelerating pace. In the final days, this decline can be brutal—options lose value even if the stock price barely moves.
📊 Case Study: The Pain of Theta
A trader buys a $50 call on XYZ stock with two weeks left until expiration. The stock barely moves, staying near $50. At purchase, the option cost $2.00, mostly made up of time value. Within a week, even though the stock is unchanged, the option is worth only $0.70. That’s a 65% loss—caused entirely by time decay.
“Time is the friend of the wonderful business, the enemy of the mediocre.”— Warren Buffett
🔗 Related Resources
If you’re comparing short-term and longer-term trades, check our guide on day trading vs swing trading . For deeper education, Investopedia’s explanation of Theta provides a professional-level breakdown of time decay in options.
⚖️ Why Time Value Matters
Many beginners make the mistake of thinking their option’s value depends only on stock movement. In reality, even a stock that moves sideways can drain your premium if you ignore time decay. Mastering Theta helps traders pick the right expirations and avoid buying contracts that will melt away before they become profitable.
Factor 3: Volatility – The Wild Card
If time is the slow burn in options trading, volatility is the sudden wildfire. It can dramatically inflate or crush the value of options, often overnight. Understanding volatility is essential for any trader hoping to profit consistently.
📌 Implied vs Historical Volatility
– Historical Volatility (HV): Measures how much the stock has fluctuated in the past. – Implied Volatility (IV): Reflects the market’s expectation of future fluctuations. IV is the key driver of option premiums—when traders expect turbulence, they bid up option prices.
⚡ The Volatility Premium
When implied volatility rises, the cost of buying both calls and puts increases—even if the stock doesn’t move. That’s why options ahead of earnings announcements or major economic reports are often far more expensive.
📊 Case Study: Earnings Season
In 2023, traders rushed to buy Apple (AAPL) calls before earnings, pushing implied volatility to record highs. The next day, Apple reported solid results, and the stock barely moved. Yet, option premiums collapsed 40–50% overnight. This wasn’t because the company disappointed, but because volatility expectations fell—a classic “volatility crush.”
“Volatility is the friend of the option buyer and the enemy of the option seller.”— Options Market Adage
🔗 Related Resources
If you want to combine volatility with technical patterns, explore our article on Elliott Waves in Trading . For market-wide volatility insights, the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) is the most trusted benchmark. For real-time market data, visit Nasdaq Options Market .
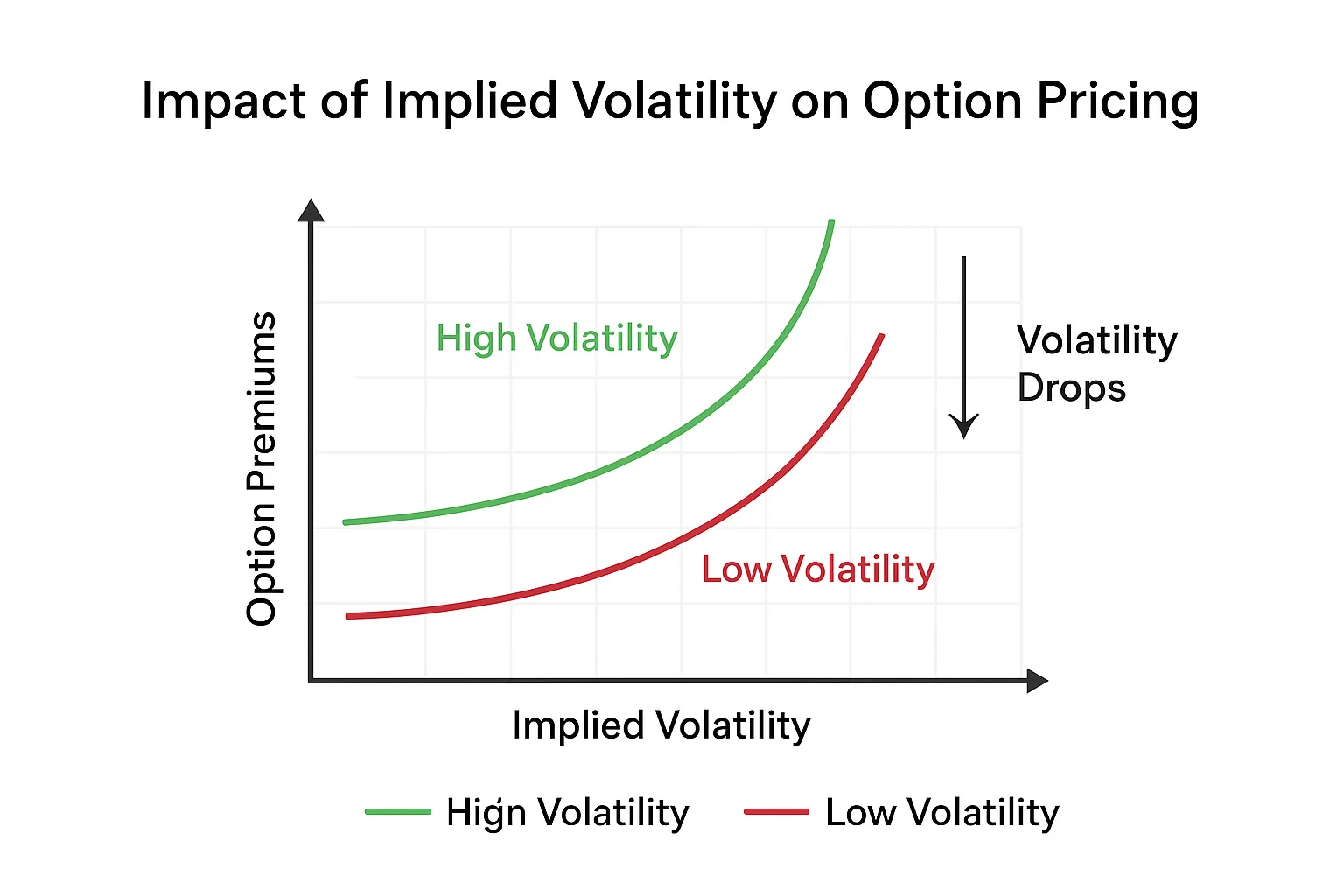
Description: A chart comparing option premiums during low-volatility vs high-volatility periods, showing the dramatic effect of IV on pricing.
⚖️ Why Volatility Matters
Volatility is unpredictable, but it is not random. Traders who ignore IV risk paying too much for options or selling them at the worst possible time. By mastering volatility, you gain an edge that separates professional-level strategies from beginner mistakes.
Factor 4: Interest Rates & Dividends
While volatility and time decay get most of the attention, interest rates and dividends also play a vital role in shaping the value of options. These two forces influence option premiums in subtle but important ways—especially for long-term traders and institutional investors.
📌 Interest Rates and the Risk-Free Rate
Options are priced partly based on the so-called risk-free rate, usually tied to U.S. Treasury yields. – When interest rates rise, call options tend to increase in value, while put options lose value. – When rates fall, the opposite effect occurs. This is because higher interest rates raise the opportunity cost of holding stock, making options relatively more attractive.
💰 Dividends and Their Impact
Dividends also affect the value of options because they reduce the underlying stock price on the ex-dividend date. – Call options lose value when dividends are paid, since the stock drops by the dividend amount. – Put options gain value from dividends, because the stock’s price decline increases the likelihood of being in-the-money.
📊 Case Study: Dividend Effect on Options
In 2022, Microsoft (MSFT) declared a $0.62 dividend. Traders holding short-dated call options saw their premiums drop overnight as the stock adjusted lower on the ex-dividend date. Meanwhile, put options with the same strike experienced a small but noticeable increase in value—an example of how dividends quietly reshape option pricing.
“Do not save what is left after spending, but spend what is left after saving.”— Warren Buffett
🔗 Related Resources
To explore how dividends can generate passive income, see our guide on income generation with dividends . For more technical analysis, the Investopedia dividend tutorial provides detailed explanations. For option pricing in global markets, Nasdaq Options Data is another reliable resource.
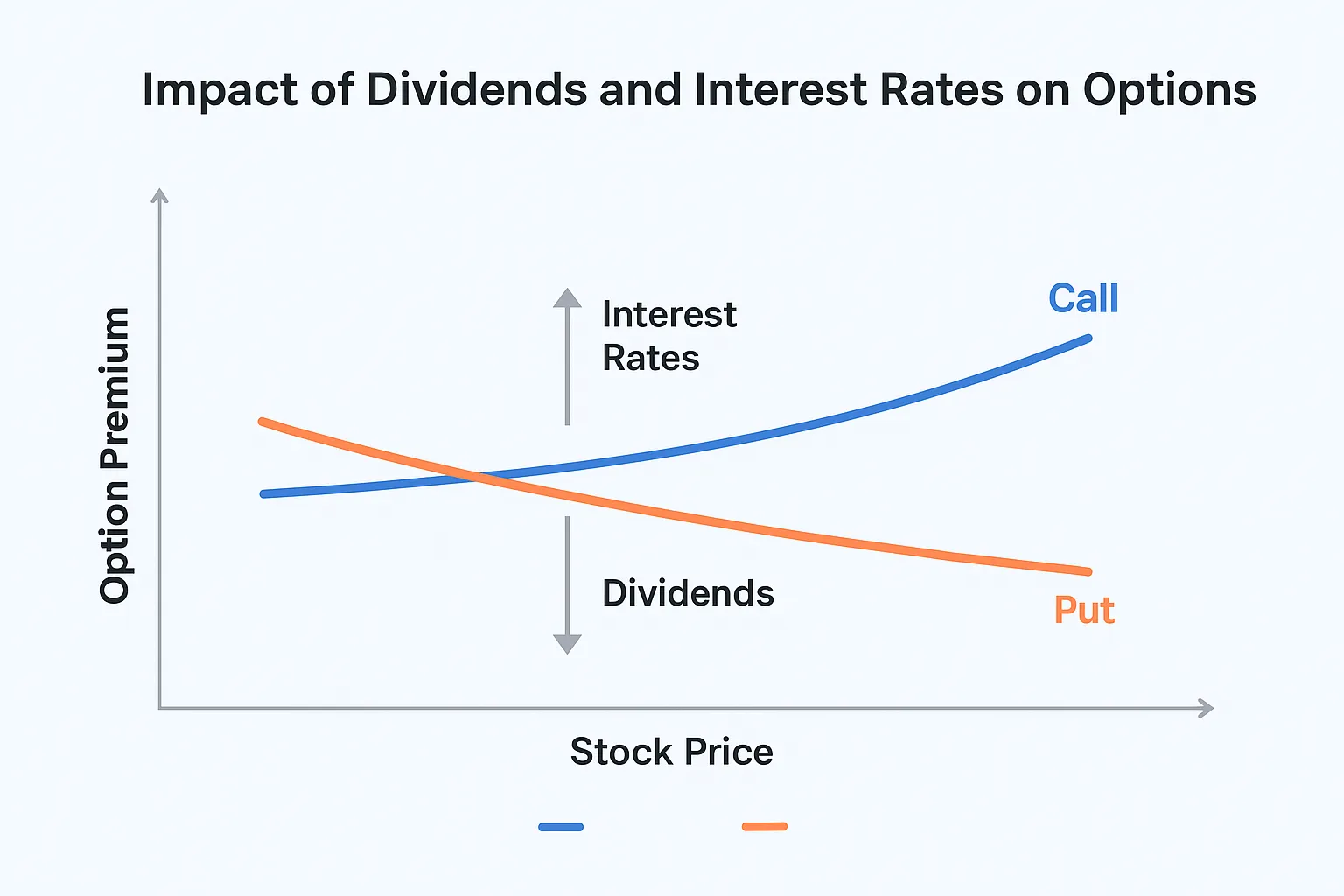
Description: A comparison chart showing the effect of rising interest rates and dividend payouts on the premiums of call and put options.
⚖️ Why Interest Rates & Dividends Matter
These factors may not dominate daily option price swings, but over time they significantly influence the fair value of options. Traders who ignore interest rates and dividends risk mispricing contracts— especially in long-term strategies like LEAPS or covered calls.
Factor 5: Supply, Demand & Market Psychology
Beyond formulas and pricing models, the value of options is ultimately shaped by human behavior. Traders’ emotions—fear, greed, and speculation—drive supply and demand in the options market, often pushing prices far from theoretical “fair value.”
📌 How Supply and Demand Affect Options
When demand for a particular strike surges, market makers raise premiums. If supply of contracts outweighs demand, prices fall. This dynamic explains why some “out of the money” calls may trade at surprisingly high levels—not because of math, but because traders are willing to pay up.
🧠 The Psychology Factor
Options trading magnifies market psychology because contracts offer leverage. – During bull runs, traders pile into speculative calls, inflating premiums. – During selloffs, demand for puts skyrockets as traders seek protection, driving up their prices. This cycle shows how emotions can override logic in determining the value of options.
📊 Case Study: The Meme Stock Frenzy
In early 2021, GameStop (GME) became the poster child of market psychology. Retail traders flooded into call options, creating historic demand. Premiums for strikes far above the current price soared to irrational levels. The surge in option buying forced market makers to hedge, which in turn pushed the stock price even higher—a feedback loop fueled entirely by speculative psychology. Traditional pricing models could not account for this, proving that supply and demand often dominate theory.
“The stock market is filled with individuals who know the price of everything, but the value of nothing.”— Philip Fisher
🔗 Related Resources
To see how bullish and bearish sentiment influences markets, explore our post on Bulls vs Bears on Wall Street . For live order flow and supply-demand dynamics, the Nasdaq Options Market is a useful resource.
⚖️ Why Psychology Matters
Even the best mathematical models can be overridden by crowd behavior. Recognizing when options are overpriced or underpriced due to market frenzy gives traders a critical edge. By monitoring sentiment, supply, and demand, you can anticipate pricing distortions and either profit from them or avoid becoming their victim.
Factors 6 & 7: Expert Insights + Real-Life Case Studies
To truly understand the value of options, it’s helpful to hear from seasoned professionals and examine real-world trades. Experts stress that theory is only half the battle— execution and psychology are just as important.
“Options pricing is never just math. It’s part science, part art, and heavily influenced by market psychology.”— Sarah Lee, Options Strategist
“Volatility is overpriced before events, underpriced after. Smart traders use that cycle to their advantage.”— Mark Reynolds, Hedge Fund Manager
📊 Real-Life Case Studies
– Apple Earnings (2023): Traders who bought short-term calls before earnings paid inflated premiums due to high implied volatility. When results were announced, the stock barely moved—but option prices collapsed, showing the danger of volatility crush.
– S&P 500 Puts During Pandemic (2020): Investors who bought long-dated puts before the March 2020 crash saw enormous gains. Here, time value and volatility worked in their favor, proving how puts can serve as insurance during systemic events.
✅ Pros & ❌ Cons of Trading Options
| ✅ Pros | ❌ Cons |
|---|---|
| Leverage allows for potentially high returns | Time decay erodes value quickly |
| Flexible strategies for income & hedging | Complex pricing models can confuse beginners |
| Hedging protects portfolios in downturns | Overpaying due to volatility crush |
| Opportunities in both bull & bear markets | High risk if mismanaged |
🔗 Related Resources
For strategies on when to trade options, see our guide on day trading alerts . Another strong read is Investopedia’s options basics for theory, and CME’s options education hub for applied insights.
⭐ Key Takeaways
- The value of options is determined by 7 powerful factors: intrinsic value, time decay, volatility, interest rates, dividends, supply/demand, and psychology.
- Expert insights prove that pricing is not just formula-based, but also shaped by market behavior and sentiment.
- Case studies highlight how events like earnings and market crashes can rapidly reshape option premiums.
- Traders should balance pros & cons before using options, aligning strategies with risk tolerance.
By combining technical knowledge with behavioral awareness, traders gain the clarity needed to approach options with confidence. The next step is practice—testing these concepts in real-world trades while managing risk carefully.