
Intel’s Investment Bid from Apple and Its Comeback Strategy Explained
Last updated • 7–9 min read
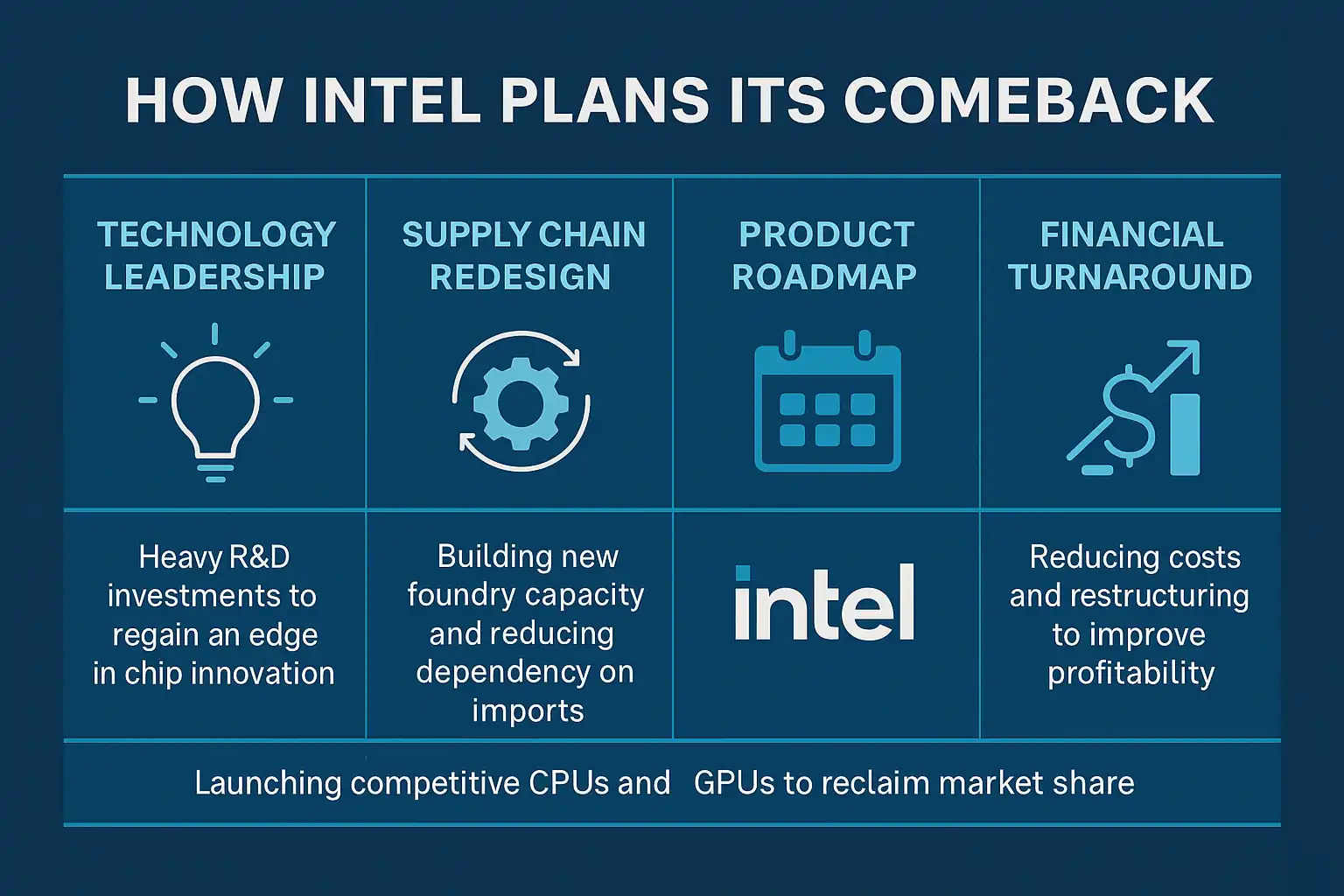
After ceding performance leadership to rivals, Intel is pursuing a multi-year turnaround built on foundry expansion, AI accelerators, and marquee partnerships. An Intel Apple investment comeback strategy could reset sentiment by securing high-volume, high-visibility demand while validating Intel’s manufacturing roadmap.
This briefing maps Apple’s potential role, the semiconductor landscape, Intel’s execution plan, key risks, and where 2025 opportunities may emerge for investors weighing U.S. tech rivalry dynamics.
Next, we break down Apple’s interest in Intel—why it matters strategically and how to track it on a live chart.
Apple’s Interest in Intel Explained
Apple’s shift toward custom silicon has transformed its product performance, but it also increased dependency on foundry leader TSMC. An Intel Apple investment comeback strategy would give Apple a diversified supply chain and help Intel secure a high-profile partner for its IDM 2.0 roadmap. For Intel, Apple represents both validation and high-margin business in a fiercely competitive semiconductor market.
According to CNBC, Apple is exploring options to invest in or collaborate with U.S. manufacturers to reduce reliance on overseas fabs. Reuters has also highlighted how Washington is encouraging this alignment under the CHIPS Act incentives.
This strategic tie-up could strengthen Apple’s bargaining power and give Intel a clearer demand roadmap. For investors, the key is whether such collaboration can meaningfully accelerate Intel’s turnaround. For deeper context, explore how traders interpret these setups in our Swing Trading Success Stories .
Next, let’s zoom out and assess the semiconductor market landscape, including how Intel stacks against Nvidia, AMD, and TSMC.
The Semiconductor Market Landscape
The chip industry remains bifurcated between design leaders and manufacturing leaders. Nvidia and AMD are sprinting ahead in AI accelerators and high-performance compute, while TSMC anchors leading-edge manufacturing for the ecosystem. Intel’s plan is to straddle both—reviving product competitiveness while scaling a merchant foundry via IDM 2.0. If an Intel Apple investment comeback strategy materializes, it could shift share-of-wallet and validate Intel’s capacity ramps in the U.S. and EU.

| Player | Core Edge | Key Watchpoints (’25) |
|---|---|---|
| Intel (INTC) | IDM 2.0 + U.S./EU capacity | Node cadence, foundry wins, any Apple alignment |
| Apple (AAPL) | Vertical integration, custom silicon | Supplier diversification beyond TSMC |
| Nvidia (NVDA) | AI accelerators & software stack | Supply elasticity, data-center demand |
| AMD (AMD) | CPUs/GPUs at competitive price/perf | Server share gains, AI GPU ramp |
| TSMC | Leading-edge foundry scale | Capacity adds, geo-diversification |
For practical timing tools during sector rotations, see Best Indicator for Swing Trading .
Next, we detail how Intel plans its comeback—from node cadence to foundry customers—before comparing live performance across INTC, NVDA, and AMD.
How Intel Plans Its Comeback (Live Peer Comparison)
Intel’s IDM 2.0 aims to regain product competitiveness while scaling a merchant foundry. A potential Intel Apple investment comeback strategy would add anchor demand and credibility. Track execution versus peers below—focusing on node cadence, data-center mix, AI accelerators, and margins.
- INTC: Watch for breakouts around product/node milestones and foundry customer disclosures.
- NVDA: Supply elasticity vs. AI demand; any margin normalization.
- AMD: Server share gains and AI GPU ramp cadence.
For a playbook on timing breakouts and managing risk around earnings and product cycles, see Best Indicator for Swing Trading .
Next, we dig into risks and execution challenges—what could derail the turnaround even with Apple’s help.
Risks and Challenges in Execution
While the Intel Apple investment comeback strategy could accelerate Intel’s turnaround, the company faces structural and execution risks. Rising R&D costs, competitive intensity, and supply chain disruptions all test management’s ability to deliver on IDM 2.0 promises.
🔬 R&D Pressure
Intel’s R&D spend exceeds $17B annually. Delays in node transitions risk eroding competitiveness. Investopedia notes how R&D efficiency can dictate semiconductor margins.
🚢 Supply Chain Complexity
Foundry expansion in the U.S. and EU faces cost inflation and skilled labor shortages. Bloomberg has reported on construction delays in Arizona fabs.
⚔️ Competitive Intensity
Nvidia and AMD continue to outpace Intel in AI accelerators and server share. Statista projects AI chip demand growth through 2030, where rivals currently dominate.
Managing these risks requires timing and patience. For real-world examples of resilience and strategy, check our Swing Trading Success Stories .
Next, we outline the opportunities for investors in 2025—where Intel could surprise on execution and reward patient shareholders.
Opportunities for Investors in 2025 (Live Market Context)
If an Intel Apple investment comeback strategy materializes, it could reset sentiment around Intel’s foundry ambitions and lift multiples across parts of the semiconductor stack. 2025 opportunities cluster around: (1) confirmation of anchor customers, (2) node cadence hitting guidance, and (3) signs of share recapture in data center and AI. Use the live charts below to gauge whether broader risk appetite (NASDAQ) and semi beta (SOXX) are supporting entries.
- IXIC uptrend + SOXX breadth: favors adding on dips to strong semi names and monitoring INTC catalysts.
- Divergence (SOXX weak vs IXIC): be selective; wait for foundry/customer confirmations before sizing up.
- Earnings / roadmap weeks: scale in thirds; use ATR/trailing stops to manage headline risk.
Want help turning these signals into trades? Explore our Day Trading Mentor and real results in Swing Trading Success Stories.
Next, we evaluate the future outlook: can Intel realistically compete with Nvidia and AMD—and on what timeline?
Future Outlook – Can Intel Compete with Nvidia and AMD? & Conclusion
Whether an Intel Apple investment comeback strategy can close the performance and ecosystem gap depends on three levers: (1) node cadence hitting guidance, (2) credible third-party foundry wins, and (3) AI product traction in data center. Nvidia still controls the accelerator stack (hardware + software), while AMD’s price/performance keeps pressure on CPUs/GPUs. Intel’s upside case requires consistent execution across multiple quarters—not a single headline.
✅ Bull Case (12–24m)
- IDM 2.0 node ramps on time; defect density improves
- Anchor customer(s) announced; Apple involvement confirmed
- AI accelerators win marquee cloud/enterprise workloads
⚖️ Base Case
- Mixed execution: progress in foundry, selective product wins
- Share stabilization in servers; desktop/mobile cyclical
- Multiple expansion hinges on guidance credibility
❌ Bear Case
- Node slips; capex overruns; delayed customer ramps
- Nvidia/AMD widen lead in AI and server share
- Margin compression; negative FCF during peak spend
Bottom line: Intel can compete if it executes consistently and secures high-credibility customers; Nvidia/AMD remain the performance benchmark. Treat headlines as signals to validate with trend, breadth, and guidance—not as standalone buy/sell triggers.
Turn the Intel Story into a Plan
Get entries, exits, and risk levels mapped to earnings and roadmap days—plus live chart setups.
Before your next trade, review our Swing Trading Success Stories and favorite Indicators for Swing Trading.

Pauline specializes in explaining how major corporate strategies—like the Intel Apple investment comeback strategy—connect to real-world trading opportunities. Her writing blends fundamentals, technical setups, and sector analysis to help both retail and professional traders capture volatility with discipline. At TradeStockAlerts.com, she focuses on tech, semiconductors, and market catalysts that drive investor sentiment.