
Bull and Bear Spreads For Options
Bull and Bear Spreads in Options Trading: Strategies to Profit in Any Market
What Are Bull and Bear Spreads in Options Trading?
— TastyTrade Instructor
If you’re new to options trading, terms like ‘bull spread’ and ‘bear spread’ might sound intimidating. But they’re simply structured strategies that combine two option legs to manage risk and maximize efficiency in directional trades.
Bull spreads are designed to profit from upward price movement with limited risk and reward, while bear spreads do the same in the opposite direction. Instead of buying naked calls or puts, these spreads offer traders a more defined approach — especially in volatile or uncertain markets.
To simplify:
- 🐂 Bull Spread: Used when you expect the stock to go up
- 🐻 Bear Spread: Used when you expect the stock to go down
📘 Key Definitions:
- Vertical Spread: Combines two calls or two puts with different strike prices
- Net Debit: You pay to open the spread (used in bull call & bear put)
- Net Credit: You receive premium upfront (used in bull put & bear call)
“Spreads let you define risk without sacrificing strategy.”
— TastyTrade Instructor
🧠 Key Takeaways:
- ✔️ Spreads reduce risk by capping both profit and loss
- ✔️ Bull spreads profit from rising stocks
- ✔️ Bear spreads profit from falling or neutral stocks
Want a refresher on how options relate to stock ownership? Check out our introduction to What Are Stocks?:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
How Bull Call and Bull Put Spreads Work
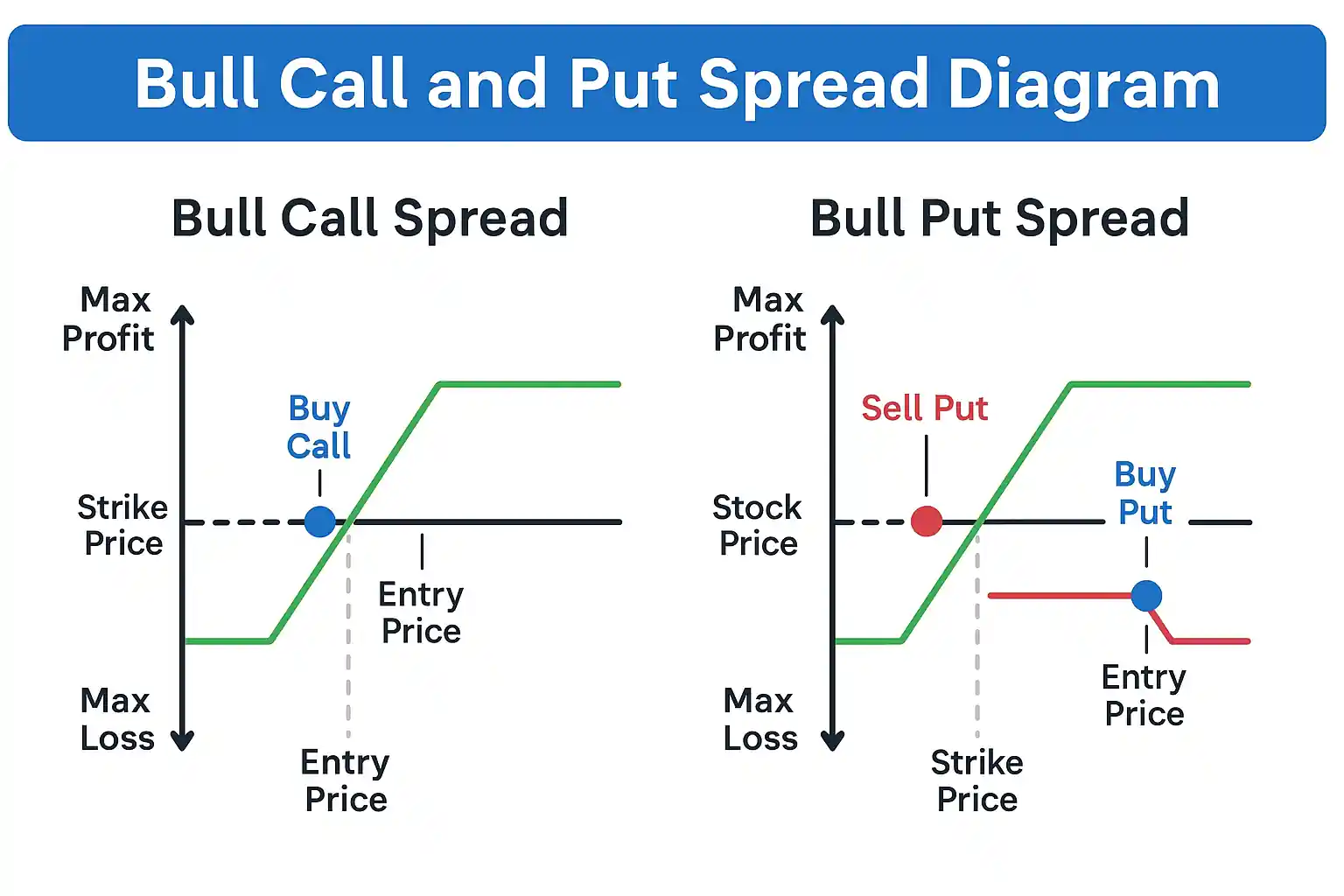
Infographic comparing bull call and bull put spreads using two-option legs, with entry price, strike price, max profit and loss visually labeled
Bull spreads are ideal when you’re moderately bullish on a stock or ETF. Instead of buying a single long call or put, these strategies combine two option legs to define both risk and reward up front.
📈 Bull Call Spread
This strategy involves buying a lower strike call and selling a higher strike call with the same expiration. You pay a net debit, and the spread profits if the stock moves up — but profit is capped.
💸 Bull Put Spread
This strategy involves selling a higher strike put and buying a lower strike put. You receive a net credit and the spread profits if the stock stays above the higher strike — or rises.
“Bull spreads are smart alternatives to long calls — lower cost, same direction, controlled risk.”
— Options Mentor & Trader, Lisa R.
✅ Pros & ❌ Cons
- ✅ Lower capital requirement than buying outright calls
- ✅ Defined risk and defined reward
- ❌ Profit is capped compared to naked options
- ❌ Can expire worthless if price doesn’t move enough
📊 Quick Example:
Suppose you open a bull put spread on Tesla with the $210/$200 strike range, collecting $2.00 in premium. As long as Tesla closes above $210 by expiration, you keep the full credit. If it drops below $200, you hit max loss — but you knew it in advance.
Want a refresher on these strategies? Check our updated breakdown on Bull and Bear Spreads for Options:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
How Bear Call and Bear Put Spreads Work
Bear spreads are ideal when you’re moderately bearish or expect a stock to stay flat or fall. Like bull spreads, these strategies combine two options to define your potential loss and gain — but in the opposite direction.
📉 Bear Call Spread
This strategy involves selling a lower strike call and buying a higher strike call with the same expiration. You receive a net credit, and your profit comes if the stock stays below the short call strike.
📉 Bear Put Spread
With this setup, you buy a higher strike put and sell a lower strike put. You pay a net debit, and the spread becomes profitable if the stock falls below the lower strike price by expiration.
“Bear spreads allow you to control premium risk when the trend turns.”
— Michael C., Senior Options Trader
✅ Pros & ❌ Cons
- ✅ Bear spreads let you profit when stocks fall or stay flat
- ✅ Both strategies clearly define your risk and reward
- ❌ Profit potential is limited by the spread width
- ❌ High volatility can increase assignment risk in bear calls
📊 Real Trade Example:
Let’s say SPY is trading at $440. You sell a $445 call and buy a $450 call, forming a bear call spread. If SPY stays below $445 at expiration, you keep the credit. If it surges above $450, you hit max loss — but it’s capped by design.
Want more context on when to use covered calls vs. spreads? Read our guide: Covered or Uncovered Options Calls:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
Real-Life Examples of Profitable Bull & Bear Spreads

Real P/L chart of a bull call spread and bear put spread setup, highlighting max profit and break-even zones
Seeing a spread in action is the best way to understand how it works. Below are two real-world options trades using bull and bear spreads that show how traders managed risk and locked in profits.
✅ Bull Call Spread on AMD
A trader anticipated a post-earnings move on AMD. Instead of buying naked calls, they used a bull call spread — buying the $95 call and selling the $105 call for a net debit of $3.50. AMD closed at $110. Max profit ($6.50) was achieved, turning $350 into $650 — nearly doubling the position.
📉 Bear Put Spread on IWM
During a pre-Fed volatility window, a trader opened a bear put spread on IWM: buy the $180 put, sell the $170 put for a $4 debit. When IWM fell to $169, the spread reached max value, resulting in a $600 net profit.
“Smart spreads are how pros take directional bets with capped downside.”
— CBOE Analyst
🔍 Lessons from These Trades:
- ✔️ Use spreads to reduce premium costs and limit risk
- ✔️ Time trades around earnings, news, or volatility events
- ✔️ Let spreads work for you even when the stock doesn’t move drastically
Want to understand how sentiment, AI, and data-driven models influenced spread setups in these trades? Read our breakdown: How AI Is Reshaping the Stock Market:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
Pros and Cons of Using Spreads in Options

Chart-style comparison of pros and cons of spreads using colored checkmarks and red X icons in two clean columns
Like any options strategy, spreads come with their own set of advantages and trade-offs. The key is understanding when they’re appropriate and how they align with your risk profile and outlook.
✅ Pros of Using Spreads
- ✔️ Limited Risk: You always know your worst-case scenario upfront
- ✔️ Lower Capital Requirement: Great for small accounts vs. naked calls/puts
- ✔️ Higher Probability Trades: Especially with credit spreads in ranging markets
❌ Cons of Using Spreads
- ❌ Profit is capped even if the trade moves in your favor
- ❌ More complexity — two legs means more to manage
- ❌ Higher commissions on some platforms for multi-leg trades
“Spreads are the Swiss Army knife of options — powerful, but only if you know how to use them.”
— Natalie F., Options Coach
Before using spreads, it’s essential to understand stock types, volatility, and market context. Learn more about this in our guide: Forms of Stocks: Common vs. Preferred:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Spreads
Even though spreads help limit risk, they’re not foolproof. Many beginner (and even intermediate) options traders make costly errors that could easily be avoided with a few key habits and planning techniques.
🚫 Mistake 1: Misjudging Max Loss
Some traders confuse net credit with maximum risk. But every spread has a defined risk amount, which depends on strike width and premium collected or paid. Not calculating this upfront can lead to unexpected outcomes.
⚠️ Mistake 2: Choosing Too Wide or Too Narrow Strike Width
Picking strikes that are too far apart may increase max gain but also raises risk and lowers probability. Going too narrow might result in minimal reward that’s not worth the trade-off.
⏳ Mistake 3: Ignoring Expiration Timing
A common misstep is holding a spread into the last days of expiration when assignment and gamma risk spike. Most professionals close positions early — often once they reach 70–90% of max profit.
“If you don’t know where your break-even is, you’re trading blind.”
— Karen Bruton, Former Hedge Fund Manager
📉 Real Example: CPI Week Chaos
During a volatile CPI release, a trader entered a bear call spread on QQQ with the $355/$360 strikes. But they forgot earnings season volatility was also in play. QQQ surged past both strikes. Because they didn’t adjust or exit early, they absorbed max loss — despite being right on direction initially.
To avoid this, many traders rely on Day Trading Alerts:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0} to time entries more precisely around macro catalysts and news.
✅ Prevention Tips:
- ✔️ Use a risk calculator before placing a trade
- ✔️ Know your break-even and worst-case scenario in advance
- ✔️ Always track volatility, earnings, and macro news when opening spreads
Best Practices for Building a Spread-Based Options Strategy
If you want to trade spreads successfully, you need more than technical knowledge — you need a repeatable process. Below are best practices used by professional traders and retail investors who consistently apply bull and bear spreads to real-market conditions.
📋 1. Start With a Clear Bias
Always know if you’re bullish, bearish, or neutral. Your directional bias determines whether you choose a bull call, bull put, bear call, or bear put spread — and what strike prices to use.
📊 2. Combine Fundamentals + Technicals
Use fundamentals to validate the setup (like earnings reports or industry trends), and then time your entry with technical indicators such as RSI, trendlines, or support/resistance zones.
⛳ 3. Choose Strike Width and Expiration Intentionally
Wider spreads offer more potential profit but require more capital. Closer expirations decay faster (good for credit spreads) but need precise timing. Don’t just “guess” — use logic and test your logic over time.
“Great spread traders think in probabilities, not profits.”
— Naresh Tharani, Market Educator
📈 4. Track and Journal Every Trade
Use a spreadsheet or tool like TraderSync or Edgewonk to record entry, exit, reason for the spread, what went right, and what went wrong. Over time, patterns emerge that help refine your strategy.
🔔 5. Use Alerts to Spot the Right Conditions
Combine spread planning with trade alerts that align with your directional bias. Many traders use Swing Trading Alerts:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0} to stay on top of breakouts and setups that are ideal for bull or bear spreads.
📌 Key Takeaways:
- ✔️ Define your outlook before selecting the type of spread
- ✔️ Use both data and timing to reduce risk
- ✔️ Review every trade — even the good ones — to learn and improve
Want pre-vetted trades tailored to spread setups? Subscribe to our service and apply spreads with confidence — not guesswork.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bull and Bear Spreads
✅ Yes. Spreads define both risk and reward in advance, which helps avoid large unexpected losses.
📊 It depends on market conditions. Credit spreads work best in sideways markets, while debit spreads perform better in trending environments.
✔️ Absolutely. With proper education, spreads are a beginner-friendly way to learn risk-managed trading.
💵 Many spreads can be opened with $100–$500 depending on the strike width and the broker’s requirements.
📚 Trusted Resources for Learning Options Spreads
📘 Investopedia: Understanding Bull SpreadsLearn the basics of call and put spreads with illustrations and trade logic. 📈 CBOE Options Strategy Library
Official strategy guides and examples from the Chicago Board of Options Exchange. 💻 NerdWallet: Best Platforms for Options Trading
Platform reviews to help you find the right broker for multi-leg strategies. 🎥 TastyTrade: Learn Options with Video
Watch real traders explain spreads, probabilities, and entry logic in plain English.
🔗 Recommended Resources for Options Spread Traders
📘 Investopedia: Understanding Bull SpreadsLearn about bull call and bull put spreads with real examples and profit/loss illustrations. 📈 CBOE Strategy Library
Official documentation on credit/debit spreads from the Chicago Board of Options Exchange. 💻 NerdWallet: Best Options Trading Platforms
Side-by-side reviews to help you choose brokers that support multi-leg spread trading. 🎥 TastyTrade: Options Trading Video Education
Watch beginner-friendly breakdowns of bull and bear spread setups with visuals and explanations.